
認識母乳活性因子gsMO
gsMO 是母乳中含量豐富的重要活性因子,在支持腸道免疫發展扮演重要的角色,幫助提升保護力。
母乳的成分不僅能滿足嬰兒生長發育 所必需的能量和營養等基本需求,文獻指出,母乳含許多不同生物活性因子(Bioactive Factors),可保護抵抗感染,幫助免疫成熟,促進組織器官發育及維護健康菌叢生態1,2。母乳之所以珍貴,因其含多種重要活性因子,如gsMO (乳源神經節苷脂, gangliosides Milk Origin),能帶給寶寶母乳獨特的活性力。
認識母乳活性因子gsMO-1
母乳生物活性因子
Human Milk Bioactive Factors

母乳的成分不僅能滿足嬰兒生長發育所必需的能量和營養等基本需求,同時還含有成分具有可保護抵抗感染,幫助免疫成熟,器官發展及健康菌叢生態等功能,這類分被稱為母乳生物活性因子(Human MilkBioactiv Factrs)。
gsMO 是母乳中含量豐富的重要活性因子之一,是由神經醯胺及含有唾液酸的寡糖鏈所構成的糖脂雙重結構。母乳中的神經節苷脂含量和比例會在哺乳期間發生變化,其含量在母乳中顯著高於一般嬰兒配方3-4。
認識母乳活性因子gsMO-2
gsMO(ganglioside Milk Origin,乳源神經節苷脂)
為母乳中含量豐富的重要活性因子之一
Gangliosides(神經節苷脂)
是由神經醯胺及含有唾液酸的寡糖所構成的糖脂雙重結構
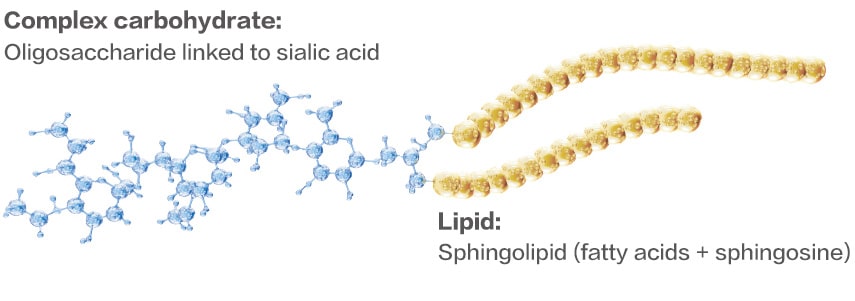
Gangliosides 分子結構
胎兒和嬰幼兒獲得神經節苷脂 (gangliosides) 有兩種途徑:自身合成和從母體中獲得,神經節苷脂可以通過胎盤屏障到達胎兒體內,而嬰兒出生後,由於嬰兒自身合成神經節苷脂的能力有限,母乳是嬰兒獲取神經節苷脂這個關鍵營養的重要來源5。
神經節苷脂廣泛分布在體內,尤其是在腸道組織及大腦中富集,它也是細胞膜的組成成分,能保護細胞膜,維持細胞膜結構及功能的完整,促進細胞膜各種酶活性恢復等作用6。
認識母乳活性因子gsMO-3
Ganglioside 來源

Obtained from the diet, such as through breastmilk

Produced endogenously (naturally by the body)
Ganglioside 廣泛分布在體内
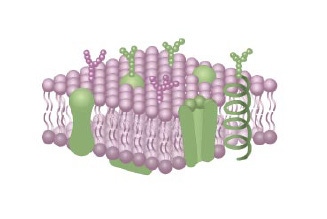
Integral to the structure and function of cell membranes
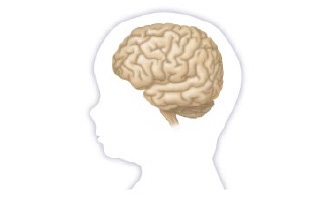
Abundant in the brain
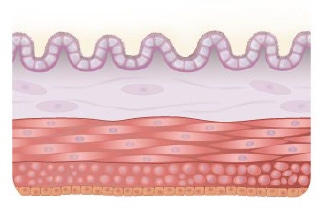
Found in the intestinal wall of the gut
母乳中含豐富的gsMO,因此,研究顯示7,嬰兒從2-8周餵養到24周,餵哺母乳的嬰兒,在6個月大時,血清中的神經節苷脂的含量較高。餵哺添加神經節苷脂奶粉的補充組嬰兒,血清中神經節苷脂含量亦顯著高於控制組(P=0.002),且與餵哺母乳的嬰兒沒有顯著差異。
認識母乳活性因子gsMO-4
母乳中的gsMO(ganglioside MilkOrigin)含量豐富
餵哺母乳的嬰兒血中的ganglioside含量較高
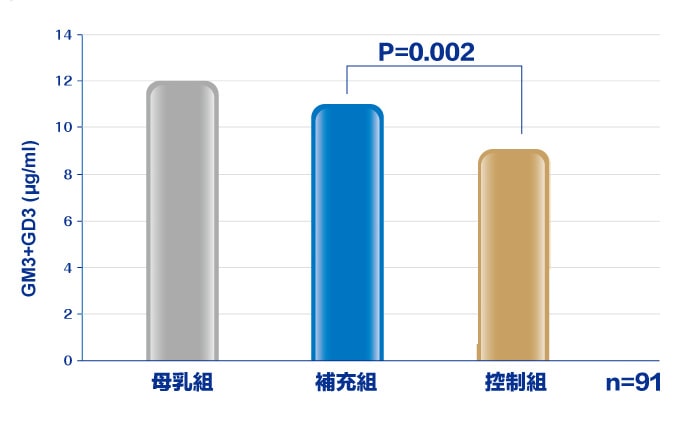
The levels of serum total ganglioside was significantly higher in the supplement(補充組) compared to the control group (控制組)(p=0.002),and notsigcd from the breastmilk group at 6 months of age.
Gumnida DA, et al. Early Hum Dev. 2012 Aug;88(8):595-601.
認識母乳活性因子gsMO-5
神經節苷脂(gangliosides)
在支持腸道免疫發展扮演重要的角色
幫助提升保護力,降低感染
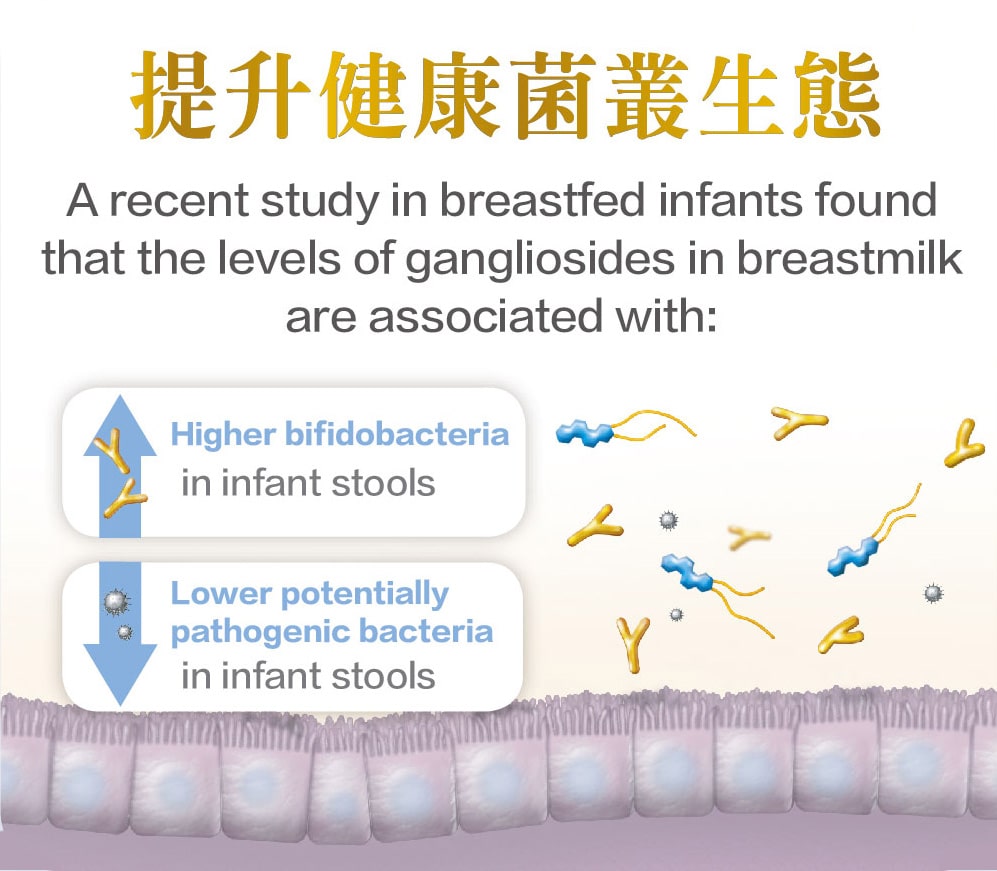
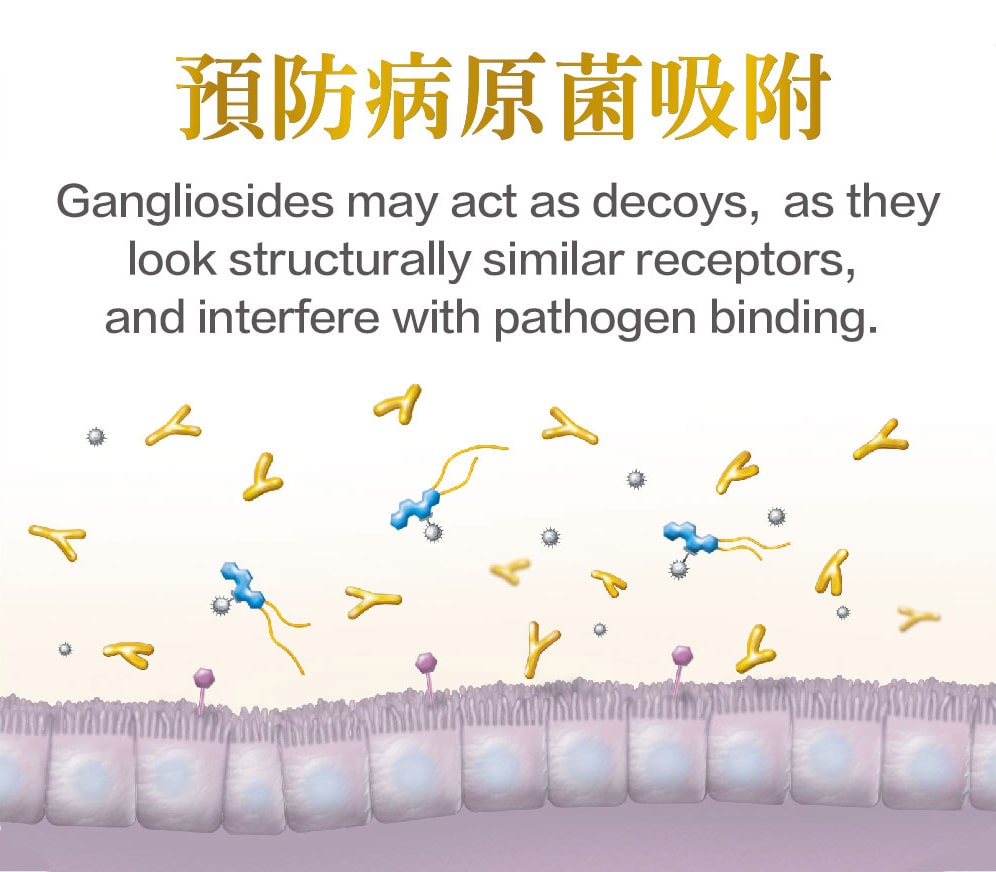

總結而言,母乳中含有gsMO,可參與嬰兒早期發展過程。飲食中添加神經節苷脂對嬰兒的早期發育相當重要,不僅能改變腸道菌叢生態,促進新生兒的腸道免疫,還可預防感染。
參考資料
- Ballard O et al. Human milk composition: nutrients and bioactive factors. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2013; 60(1):49-74.
- Aly E. ey al. Bioactive Components of Human Milk: Similarities and Differences between Human Milk and Infant Formula, Selected Topics in Breastfeeding, November 5th 2018
- Giuffrida F, Cruz-Hernandez C, Bertschy E, et al. Temporal changes of human breast milk lipids of Chinese mothers. Nutrients. 2016;8(11):715.
- Pan XL & Izumi T. Variation of the ganglioside compositions of human milk, cow’s milk and infant formulas. Early Hum Dev.2000;57, 25-31.
- Yu RK, Tsai YT, Ariga T, Yanagisawa M. Structures, biosynthesis, and functions of gangliosides-An overview. J Oleo Sci. 2011;60(10):537-44.
- Park EJ, Suh M, Ramanujam K, Steiner K, Begg D, Clandinin MT. Diet-induced changes in membrane gangliosides in rat intestinal mucosa, plasma and brain. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005;40(4):487-95.
- Gurnida DA, et al. Association of complex lipids containing gangliosides with cognitive development of 6-month-old infants. Early Hum Dev. 2012 Aug;88(8):595-601.
- Rueda R. The role of dietary gangliosides on immunity and the prevention of infection. Br J Nutr. 2007;98(Suppl 1):S68-73.
僅供專業醫事人員使用